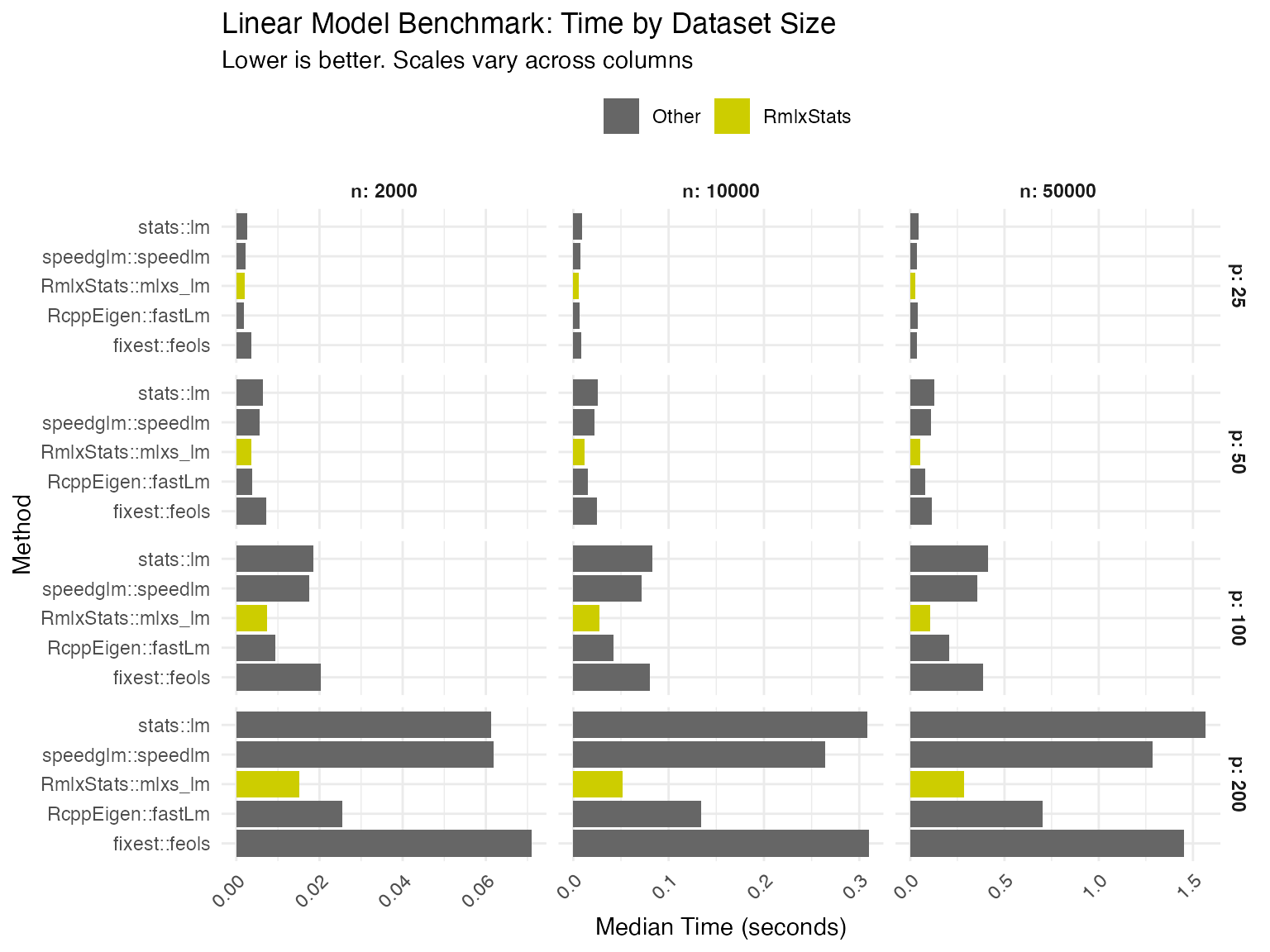
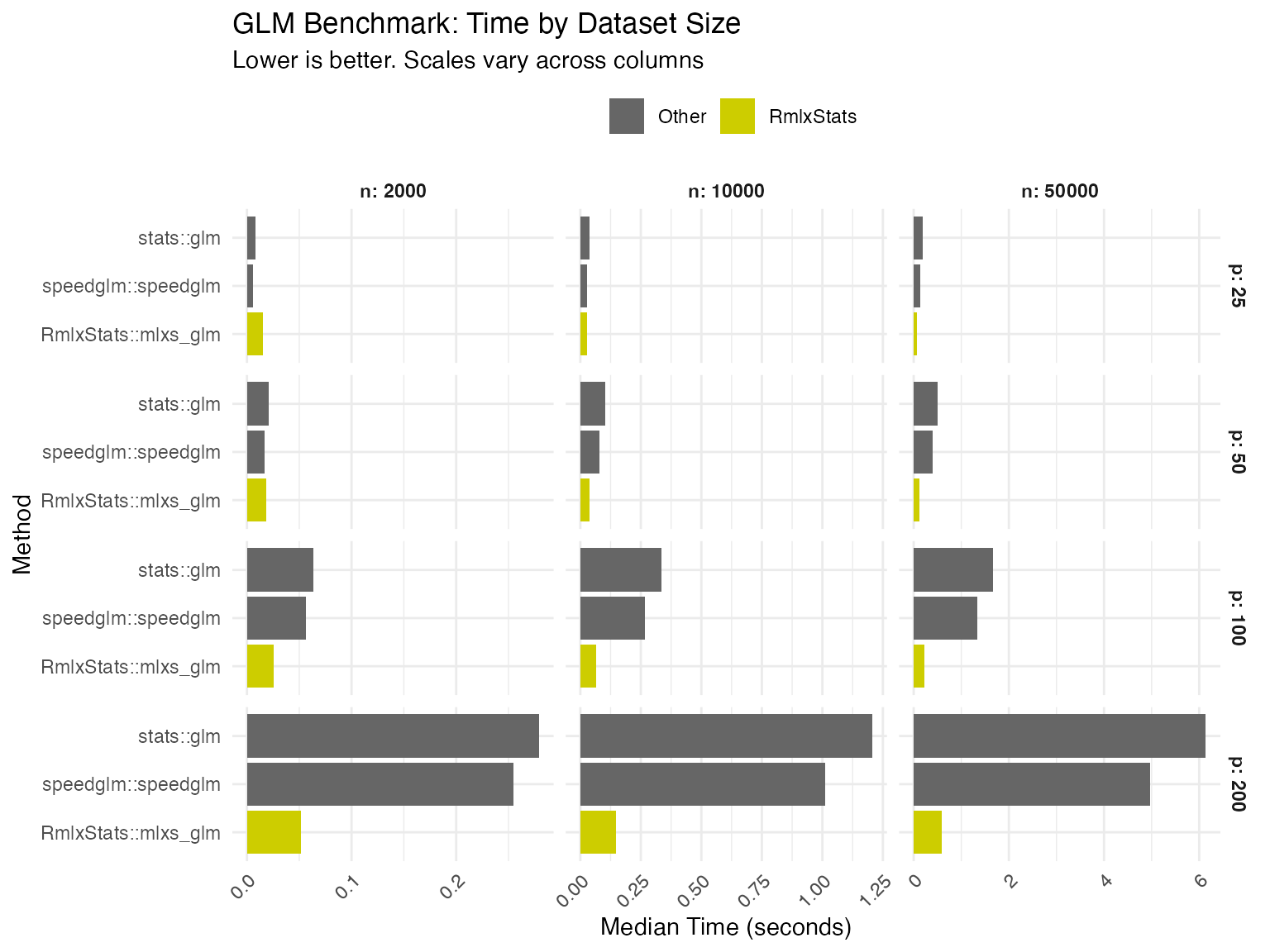
We benchmark RmlxStats against base R and specialized fast fitting
packages, across varying numbers of cases (n) and
predictors (p).
Benchmarking was run on an M1 Macbook Air.
Data Generation
set.seed(20251111)
n_max <- 50000
p_max <- 200
X <- matrix(rnorm(n_max * p_max), nrow = n_max, ncol = p_max)
colnames(X) <- paste0("x", seq_len(p_max))
beta_true <- rnorm(p_max, mean = 0, sd = 0.5)
y_continuous <- drop(X %*% beta_true + rnorm(n_max, sd = 2))
linpred <- drop(X %*% beta_true) / 5
prob <- 1 / (1 + exp(-linpred))
y_binary <- rbinom(n_max, size = 1, prob = prob)
full_data <- data.frame(
y_cont = y_continuous,
y_bin = y_binary,
X
)
n_sizes <- c(2000, 10000, 50000)
p_sizes <- c(25, 50, 100, 200)
# for fast debugging
if (params$develop) {
p_sizes <- p_sizes/10
n_sizes <- n_sizes/10
}
bench_grid <- expand.grid(
n = n_sizes,
p = p_sizes,
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
bench_grid <- bench_grid[bench_grid$n > bench_grid$p, ]Linear Model Benchmarks
lm_results <- list()
for (i in seq_len(nrow(bench_grid))) {
n <- bench_grid$n[i]
p <- bench_grid$p[i]
subset_data <- full_data[1:n, c("y_cont", paste0("x", 1:p))]
formula_str <- paste("y_cont ~", paste(paste0("x", 1:p), collapse = " + "))
lm_formula <- as.formula(formula_str)
bm <- mark(
"stats::lm" = lm(lm_formula, data = subset_data),
"RmlxStats::mlxs_lm" = {
l <- mlxs_lm(lm_formula, data = subset_data)
Rmlx::mlx_eval(l$coefficients)
},
"fixest::feols" = feols(lm_formula, data = subset_data),
"RcppEigen::fastLm" = RcppEigen::fastLm(lm_formula, data = subset_data),
"speedglm::speedlm" = speedglm::speedlm(lm_formula, data = subset_data),
iterations = 3,
check = FALSE,
filter_gc = FALSE
)
bm$n <- n
bm$p <- p
bm$model_type <- "LM"
lm_results[[i]] <- bm
}
lm_df <- do.call(rbind, lm_results)GLM Benchmarks
glm_results <- list()
for (i in seq_len(nrow(bench_grid))) {
n <- bench_grid$n[i]
p <- bench_grid$p[i]
subset_data <- full_data[1:n, c("y_bin", paste0("x", 1:p))]
formula_str <- paste("y_bin ~", paste(paste0("x", 1:p), collapse = " + "))
glm_formula <- as.formula(formula_str)
bm <- mark(
"stats::glm" = glm(glm_formula, family = binomial(),
data = subset_data,
control = list(maxit = 50)),
"RmlxStats::mlxs_glm" = {
g <- mlxs_glm(glm_formula, family = mlxs_binomial(),
data = subset_data,
control = list(maxit = 50, epsilon = 1e-6))
Rmlx::mlx_eval(g$coefficients)
},
"speedglm::speedglm" = speedglm::speedglm(glm_formula, family = binomial(),
data = subset_data),
iterations = 3,
check = FALSE,
filter_gc = FALSE
)
bm$n <- n
bm$p <- p
bm$model_type <- "GLM"
glm_results[[i]] <- bm
}
glm_df <- do.call(rbind, glm_results)Bootstrap Benchmarks
For bootstrap, we use only the smaller datasets due to computational cost.
boot_grid <- expand.grid(
n = n_sizes[1:2],
p = p_sizes[1:3],
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
boot_results <- list()
for (i in seq_len(nrow(boot_grid))) {
n <- boot_grid$n[i]
p <- boot_grid$p[i]
subset_data <- full_data[1:n, c("y_cont", paste0("x", 1:p))]
formula_str <- paste("y_cont ~", paste(paste0("x", 1:p), collapse = " + "))
boot_formula <- as.formula(formula_str)
fit_mlxs <- mlxs_lm(boot_formula, data = subset_data)
fit_base <- lm(boot_formula, data = subset_data)
# Bootstrap function for boot package
boot_stat <- function(dat, idx) {
coef(lm(boot_formula, data = dat[idx, , drop = FALSE]))
}
bm <- mark(
boot_case = boot::boot(subset_data, statistic = boot_stat,
R = 50L, parallel = "no"),
lmboot_case = lmboot::paired.boot(boot_formula, data = subset_data,
B = 50L),
lmboot_resid = lmboot::residual.boot(boot_formula, data = subset_data,
B = 50L),
mlxs_case = {
s <- summary(fit_mlxs, bootstrap = TRUE,
bootstrap_args = list(B = 50L, seed = 42,
bootstrap_type = "case",
progress = FALSE))
Rmlx::mlx_eval(s$std.err)
},
mlxs_resid = {
s <- summary(fit_mlxs, bootstrap = TRUE,
bootstrap_args = list(B = 50L, seed = 42,
bootstrap_type = "resid",
progress = FALSE))
Rmlx::mlx_eval(s$std.err)
},
iterations = 3,
check = FALSE,
filter_gc = FALSE,
memory = FALSE
)
bm$n <- n
bm$p <- p
bm$model_type <- "Bootstrap"
boot_results[[i]] <- bm
}
boot_df <- do.call(rbind, boot_results)Summary Tables
We compare RmlxStats functions both against base R, and against the
fastest alternative tested. Numbers show
RmlxStats time/alternative time.
| n=2000, p=25 | n=10000, p=25 | n=50000, p=25 | n=2000, p=50 | n=10000, p=50 | n=50000, p=50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Model | 78.0 | 65.4 | 63.3 | 57.8 | 46.7 | 40.9 |
| Logistic Regression | 197.4 | 71.3 | 33.9 | 90.7 | 35.9 | 22.5 |
| Bootstrap (Case) | 34.5 | 26.7 | 26.6 | 21.2 | ||
| Bootstrap (Residual) | 166.2 | 87.6 | 77.0 | 41.6 | ||
| n=2000, p=100 | n=10000, p=100 | n=50000, p=100 | n=2000, p=200 | n=10000, p=200 | n=50000, p=200 | |
| Linear Model | 40.3 | 32.5 | 25.9 | 24.7 | 16.7 | 18.2 |
| Logistic Regression | 40.2 | 19.4 | 13.6 | 18.6 | 12.1 | 9.6 |
| Bootstrap (Case) | 18.9 | 16.2 | ||||
| Bootstrap (Residual) | 30.1 | 22.9 |
| n=2000, p=25 | n=10000, p=25 | n=50000, p=25 | n=2000, p=50 | n=10000, p=50 | n=50000, p=50 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Linear Model | 113.7 | 85.7 | 77.5 | 96.9 | 76.2 | 65.5 |
| Logistic Regression | 250.8 | 98.1 | 47.4 | 111.9 | 46.3 | 28.8 |
| Bootstrap (Case) | 44.7 | 26.7 | 26.6 | 21.2 | ||
| Bootstrap (Residual) | 166.2 | 87.6 | 77.0 | 41.6 | ||
| n=2000, p=100 | n=10000, p=100 | n=50000, p=100 | n=2000, p=200 | n=10000, p=200 | n=50000, p=200 | |
| Linear Model | 79.4 | 64.3 | 52.0 | 59.5 | 38.5 | 40.5 |
| Logistic Regression | 45.8 | 24.3 | 16.9 | 20.4 | 14.4 | 11.9 |
| Bootstrap (Case) | 18.9 | 16.2 | ||||
| Bootstrap (Residual) | 30.1 | 22.9 |